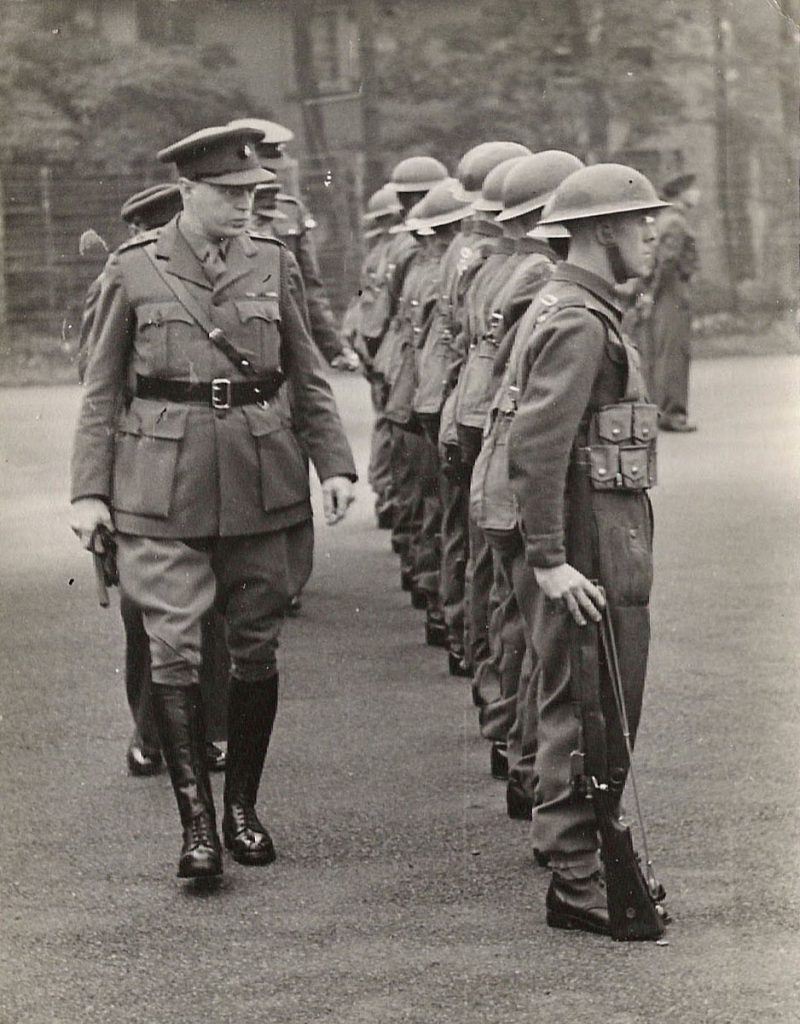

One of the pleasures of running coldspur is the fact that so many interesting people stumble across it, and contact me. Apart from the dozens of professional and amateur enthusiasts of intelligence and espionage matters, a number of individuals with intriguing backgrounds have written to me: for example, a retired counter-intelligence officer overseas; a man who lodged with Agent SONIA in Great Rollright as a boy; a grand-daughter of the MI5 officer Michael Serpell; the son of the FBI’s representative in London during the Fuchs events; a son of the Communist spy Dave Springhall, who only recently learned who his father was; and, recently, the grandson of a soldier who guarded interned spies at a Home Office internment camp in World War 2.
It is the last whose story I want to highlight in this month’s feature. I believe that Pete Mackean owns a startling set of photographs from Camp 020 in its four incarnations, at Latchmere House, Huntercombe Park, Diest and Bad Nenndorf, some of them showing notable figures involved in the administration of the camps that have not been published before. They deserve a wider audience. When Pete shared them with me, I immediately suggested that coldspur might be a good place to showcase them, and he graciously agreed to let me use them.

Yet I wanted to place them in a solid context. I was familiar with Latchmere House at Ham in Surrey, partly because I had played golf in the grounds next to it. I had also encountered the history of Camp 020 (as it became to be called) from the work issued in 2000 by the Public Record Office (as it then was), Camp 020: The Official History of MI5’s Wartime Interrogation Centre, compiled from the accounts of Lieutenant-Colonel R. W. G. Stephens and his assistants Lieutenant-Colonel G. Sampson and Major R. Short, and edited with an introduction by Oliver Hoare. Camp 020, otherwise known as Latchmere House, is a well-known landmark in counter-espionage literature. During World War II, it was used as a detention and interrogation centre for suspected German spies (most of whom, incidentally, were not German citizens), as well as, for a short time, a place to intern obvious domestic subversives, such as Oswald Mosley. It was led by the celebrated Lieutenant-Colonel R. W. G. Stephens, known as ‘Tin-Eye’ because of his monocle.
But Huntercombe, the alternative and back-up partner to Camp 020, which was dubbed Camp 020R, was much of a mystery to me, and I wanted to research its provenance and development in more detail. It was intended by Stephens and MI5 that there should not be any sharp distinctions made between the Camp 020 and Camp 020R. Yet a study of the files at the National Archives (specifically, KV 4/102 & /103) reveals that Huntercombe took on an identity and life of its own, and was not just an extension, or potential replacement, for Camp 020. (The ‘R’ stood for ‘Reserve’.) Its story has been largely overlooked.
Huntercombe merits only one paragraph (and a very occasional reference) in Stephens’s history: Christopher Andrew ignores it completely in his authorised history of MI5, Defence of the Realm, while John Curry briefly records, in his official history of MI5, that Camp 020 and 020R were in fact a ‘joint establishment’. Hinsley and Simkins, in Volume 4 of British Intelligence in the Second World War, merely cite, in an Appendix, when it was opened, as a reserve camp, in January 1943. In MI5, Nigel West suggests that ‘a long-term detention centre was hastily sited at a quiet spot on Lord Nuffield’s estate, Huntercombe Place, Nettlebed, near Henley’, an assessment that turns out to be incorrect on several counts. Guy Liddell, in his Diaries, makes one or two references to Huntercombe specifically, but his generic mentions of ‘Camp 020’ could be intended to designate either of the two.
As background reading, I heartily recommend A. W. Brian Simpson’s In The Highest Degree Odious (1992), a magisterial account of the slide into aggressive detention policy in the first years of the war. (Its major defect for me was an abundance of Footnotes, a tide that became highly distracting. Most of them should have been packaged as Endnotes. I also believe that Simpson is a little harsh on MI5, since his criticisms of it cover exactly the time that it was essentially leaderless, under Lord Swinton’s Security Executive, from May 1940 to March 1941.) Hinsley and Simkins give an overall solid account of the legislative muddles that accompanied the establishment of Camp 020, although they cover very superficially the implications of the Treachery Act. Helen Fry’s London Cage (2017) is a very useful guide to the string of prisons and detention centres where German prisoners-of-war were interrogated.
As a final observation on the slimness of official accounts, I have found no single place where all the Camps referred to in the literature (001- Dartmoor, 011- Bridgend, 020 – Ham, 020R – Huntercombe, 186 – Colchester, L – Isle of Man, WX – Stafford Prison, and then the Isle of Man, X – Canada, Z – Aldershot) are listed and described. A sentence on the Kew website runs as follows: “Those classified in Category A were interned in camps being set up across the UK, the largest settlement of which were on the Isle of Man though others were set up in and around Glasgow, Liverpool, Manchester, Bury, Huyton, Sutton Coldfield, London, Kempton Park, Lingfield, Seaton and Paignton. Other documents indicate that there was not a direct correspondence between identified camps and named prisons: for example, Camp001 was the isolated hospital wing at Dartmoor.
The Background – Dealing with Hostile Elements:
Great Britain, primarily represented by the Home Office, struggled with the challenge of controlling and defanging undesirable elements in the first year of the war. The problem was multi-dimensional. In one category were British citizens who held unreliable opinions – the Fascist sympathisers, such as Oswald Mosley’s British Union, and The Link; communists driven into a hostile position by the demands of the Nazi-Soviet Pact, who might undermine the war effort; pacifists who, out of different convictions, might spread similar disaffection. In the second category were aliens, including German (and other) citizens who had fled from Nazi-controlled territories before the war, refugees escaping from territories that had succumbed to Nazi invasions in the first half of 1940, as well as unfortunate Germans and Austrians who had settled unobtrusively in the country during the last decade or two. The Home Office had no confident means of distinguishing between those fiercely opposed to Hitlerism, those who may have been infiltrated as spies or subversives, and those essentially apolitical beings who had switched their national loyalties. (This problem became more absurd when Italy entered the war in June 1940.) In the third category were true spies, who entered the country illegally or clandestinely (or, later in the war, were picked up on territories abroad), were not protected by any military uniform, and presented a unique challenge since no appropriate laws had been set up for their treatment, and, because of MI5’s peculiar interest in them, presented some problems for any open prosecutorial process.
The problem of handling subversive citizens had been addressed by some clumsy amendments to general Defence Regulations, most notoriously Amendment 39A, and a new paragraph 1a to 18B, which was introduced in May 1940. This allowed detention of any persons who were found to be furthering the objectives of the enemy, and resulted in many prominent citizens (such as Oswald Mosley) being detained in prison. As Simpson wrote, anyone to whom the Home Secretary took exception could be locked up for an indefinite period. Yet the policy took on a sharper focus in the summer of 1940. Mass internment of persons of German origin began after the Fifth Column scare of early June, 1940, and special camps, such as on the Isle of Man, were set up to hold such groups. Since the centuries-old Treason Act required special rules of evidence and procedure (and foreign spies, unlike those who has sought asylum, could hardly be accused of treasonable behaviour against a country to which they owned no allegiance), a Treachery Bill was quickly formulated, and passed on May 23. It likewise demanded the death penalty, but it could be commuted.
The outcome of this combination of respect for legal procedure, and somewhat panic-driven haste, was that a mixture of irritating but probably harmless ruffians, possible traitors sympathetic to Germany, suspicious but maybe innocent foreigners, and certifiably dangerous spies and saboteurs sometimes found internment in the same location. Ascot Racecourse was one internment camp, as were the Oratory Schools: Wandsworth and Holloway jails were also used. In January 1941, the Royal Victoria Patriotic Schools building in Wandsworth was set up as a general reception function (the London Reception Centre) for all manner of aliens, under the responsibility of the Home Office, but with MI5 conducting the interrogations, and the Army providing the guards and sentries. In mid-July, 1940, Latchmere House opened, and as Professor Hinsley wrote, ‘accepted its first batch of enemy aliens, British fascists, and suspects arriving from Dunkirk’. Yet the awareness of habeas corpus, and the inability of the government to hold suspects for more than twenty-eight days, led to vociferous complaints by the British citizenry among this group, declaring their entitlement to a fair trial, meant that a change of policy occurred. The crux of the matter was that internees could be interrogated, but those prosecuted could not.
As Hinsley went on to write (Volume 4, p 70): “Latchmere House had been opened as an interrogation centre for suspect Fifth Columnists in July, but in October MI5 decided that it should be used only for more serious cases among aliens, for example where espionage was suspected, and that British subjects should be taken there only in very exceptional circumstances. And from early in November the place was entirely reserved for captured agents, including some of the double-cross agents, arrangements being made by which MI5 reported to the Home Office every month the names of those detained, the reason for their detention, and the length of time they had been there.” Early the following year, as the double-cross operation gained momentum, the danger of leakage about the whole process impelled the authorities to decide that Latchmere House could not be used as a holding-place for short-term interrogation. It gained the nomenclature of ‘Camp 020’ in December 1941, and was by then assigned to the permanent detention of captured agents and dubious refugees, even though many were sent on to other secure areas, such as Dartmoor Prison (Camp 001), or Camp WX on the Isle of Man.
Since one of the primary functions of Camp 020 was to weed out dedicated Nazi agents, with the possibility of ‘turning’ suitable candidates to work for the British, it took on a highly secret nature, since, if an agent was detained, and then found not be suitable for turning, or betrayed that trust, MI5 could not risk any inkling of that attempt to leak out to the enemy. The initial policy for Camp 020 was to hold detainees incommunicado: that was one of the key differences between internment and imprisonment. (In September 1941, a potential disaster was averted after the failed double-agent JEFF had been sent to Camp WX, next to Camp L, on the Isle of Man, where Nazi German internees were held.) Moreover, complications were caused by the fact that, if any such victim were sent to trial, officers at Latchmere House would be called upon to give evidence. Proceedings and interrogations were documented in secrecy: if a formal statement were required, officers would have to send the subject to one of the prisons. Permanent detention was thus preferred to open prosecution. Permanent detainees could be housed in conventional prisons, but run-of-the-mill offenders could not be detained indefinitely in Camp 020.

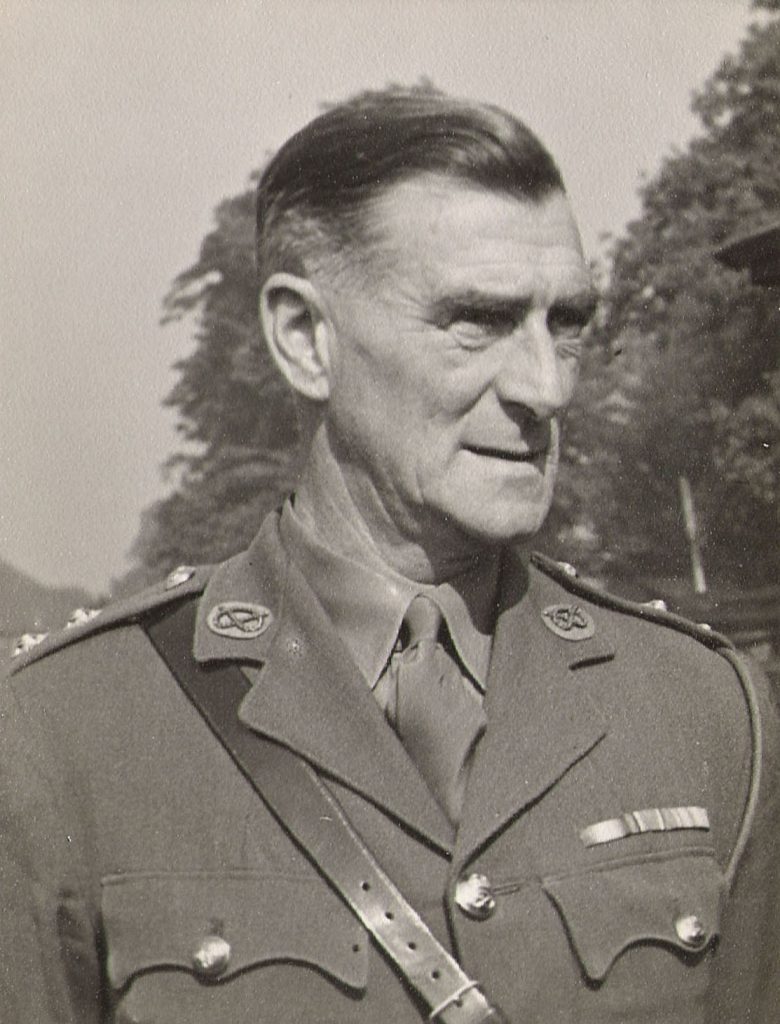
Rumours about the prolonged interrogation and detention in 1943 would cause questions in high places to be posed about whether MI5 was under proper ministerial control. Indeed, up till then, Camp 020 had been running in an extra-legal fashion, much to the embarrassment of the Home Secretary, John Anderson. Nigel West points out that it was omitted from the list of camps submitted to the Red Cross, and thus was protected from inspection. MI5 survived that investigation, and several probable spies – though many who had been captured overseas could not be convicted of offenses against Great Britain, and had to wait until the end of the war to be repatriated – remained in detention for years. As Hinsley wrote: “Once a man’s case was completed, if he was not executed, released as innocent, or released to B1A to act as a double-agent. life in Camp 020 was far from intolerable.” (Hinsley overlooks the fact that some prisoners were despatched to other camps.) And that was the fate of the overwhelming majority of those sent to Camp 020.
From various comments in his Diaries, Guy Liddell betrays some of the tensions experienced in trying to keep the lid on the activities at Camp 020, away from the prying eyes of diplomats and bureaucrats. The main objective seemed to be to ensure that no whisper of information about the Double Cross initiatives – especially of those who had been initially considered, and exposed to the scheme, but then turned out to be unreliable – must be allowed to travel outside. Hence the emphasis on keeping prisoners incommunicado, and not releasing them for trial. Liddell makes references to more candidates who were offered the chance, but then failed the test. They had to be locked away. Moreover, MI5 took big risks with Agent ZIGZAG, Edward (Eddie) Chapman, who was brought back to Camp 020 for interrogations after undertaking missions abroad.
The Idea Behind Camp 020R:
The sense of awkwardness about Camp 020R may have been due to the fact that it had become an expensive white elephant. It was originally conceived as a back-up in the event that Latchmere House were bombed. A minor aeronautical raid in January 1941 had exposed the establishment, as if the Germans knew what was going on there. Stephens wrote as follows: “In consequence the Commandant was instructed to plan a duplicate camp at Nuffield. Thus Huntercombe, or Camp 020R, came into being. Primarily it was intended as a reserve camp. It was large enough to absorb Ham in time of crisis and to provide for the future commitments of a long-term war. It included a hostel at Wallingford where some 80 female staff could be accommodated. The decision was wise, but the cost, about £250,000, was high, and it is for consideration whether M.I.5. should not have a permanent lien on the place. In the event, Huntercombe was never put to full use as the Germans were good enough to leave Ham alone. The camp, however, did become the oubliette *; the place where enemy spies, no longer of interest, were allowed to vegetate until the end of the war.”
[* Oubliette: ‘a dungeon with no opening except in the roof’ (Chambers Dictionary, from the French ‘oublier’, to forget. Obviously a very un-English form of punishment)]
A study of KV 4/102 & 4/103 at the National Archives tells a rather more complicated story. Brigadier Harker had been discussing with Lord Swinton, the Chief of the Security Executive, as early as December 1940, the acquisition of ‘another complete establishment in the country’, concurrently with plans to construct new cells near the existing Latchmere House building. Early in 1941, waves of fresh German spies were expected. Army GHQ was concerned about the location and exposure of Ham, and the War Office began pressing Lord Swinton for an ‘alternative Latchmere’ in February. Swinton concurred: Latchmere had almost been hit again that month.
Thus negotiations began. The Home office and the Ministry of Works had to be involved. A March 10 memorandum to R. S. Wells at the Home office by D. Abbot states: “So far as the area of search [for premises] is concerned we must be guided by Home Forces. For our part we would like to be somewhere well outside London, and if possible in the general direction of Oxford. Or perhaps more broadly speaking within a sector bounded by lines drawn due West and N.N. West from London.” The search began. The Ministry of Works recommended a site, The Springs, North Stoke, in Oxfordshire, but it was deemed unsuitable.
The Selection of a Site:
By May 1, however, a more attractive site (for what was then called ‘Latchmere R’) had been found, and the Post Office was asked to be involved, as it would need setting up the same listening equipment that existed at Camp 020. Here we also find a mention of a ‘Home for Incurables’, suggesting that some diehard prisoners might be accommodated on the new premises, and require special handling in a facility some 200 or 300 yards from the main building. The site is not yet identified, but a report says that ‘the present owner, who is anxious to get rid of the place, has offered it for sale for £25,000, but the Ministry of Works . . . would requisition it under their present powers probably at a rental of £200 or £300 per annum.’
The site is soon identified as Huntercombe Place, owned by Sir Francis Maclean. Maclean had been a WWI air ace, and was now Sheriff of Oxfordshire. He was famous for an aviation feat on August 10, 1912, when he flew his biplane through Tower Bridge, and under several other bridges on the Thames (see https://www.thisdayinaviation.com/10-august-1912/ ) Sir Francis wanted to stay in the Mansion House until the end of the year, but he was told that the outbuildings would need to be possessed immediately.
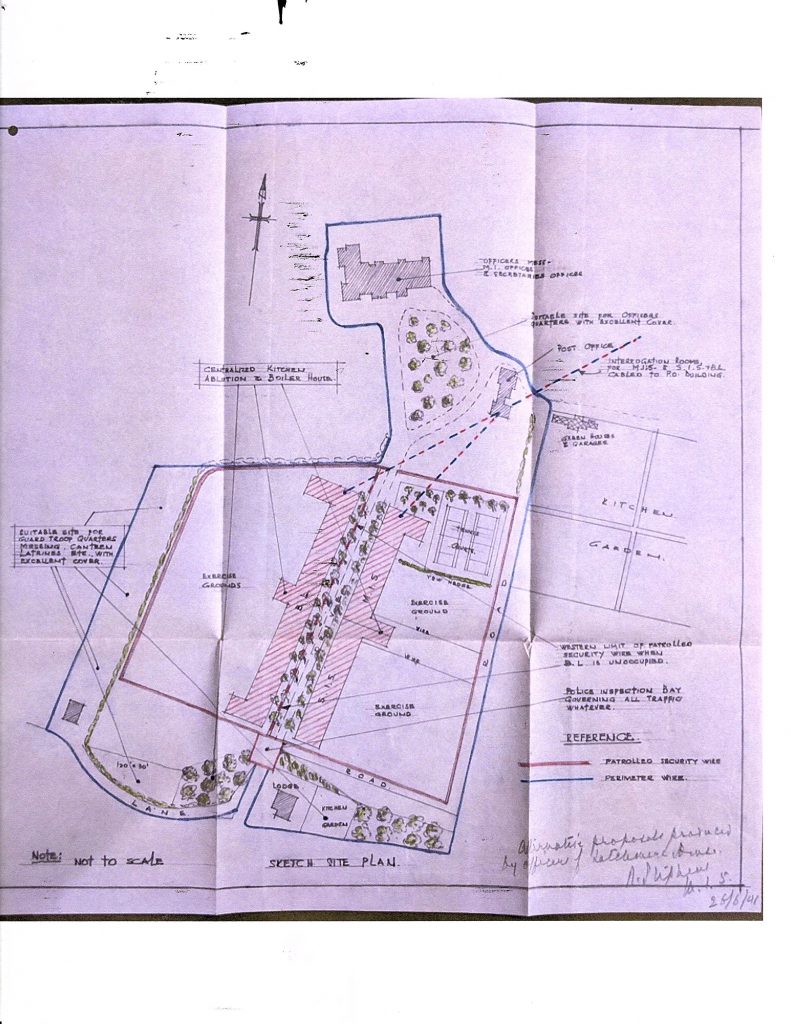
Stephens visited the site in the middle of June, and was impressed with the location, the seclusion it offered, and the general amenities. But he was not so happy with the emerging plans for replicating Latchmere House, and the amount of personnel it would take to guard the place properly. On June 23, he wrote to Richard Butler (of the MI5 Secretariat) that his plans would turn out to be cheaper than those of the Ministry of Works: his suggestion can be seen alongside that of the Ministry. Lord Swinton chipped in at the end of the month, indicating that the back-up site was more urgent than the ‘Home for Incurables’, and stressing the need for speed.
Yet, despite all the apparent urgency, obstacles started to appear for what was now being called ‘Nuffield Camp’. The War Office was under the impression that the shadow camp would be occupied only if Ham were evacuated, and therefore no new guard personnel would be required. Stephens had to somehow finesse the problem that the separate oubliettes required by MI5 and SIS would come into operation immediately, while the shadow Prison block for Latchmere House would come into operation when Latchmere House was irretrievably ‘blown’, which went very much against Lord Swinton’s view of things. Moreover, the Ministry of Works was dragging its feet, and the optimum building season was, by July, passing by.
Stephens had a clash with the ‘pessimist’ Russell, of the Ministry of Works, who was slow visiting the site. They disagreed about the availability of labour, and Stephens was impelled to write a letter to Butler, complaining about the delays, saying that ‘the completion of Latchmere “R” ten months hence [i.e. May 1942] will be of little use to the Security Services’, when Swinton had hoped for completion by October 1941. Stephens was still referring to the need for the ‘reserve’ camp in terms of Latchmere House’s staff and prisoners moving ‘in the event of an invasion, or if it should again suffer from enemy action’. Yet he must have known by then, what with Germany’s invasion of the Soviet Union in June, that both threats were drastically reduced.
Lord Swinton Intervenes:
And then a further blow occurred. There had obviously been rumblings about who should pay for the construction, and it was agreed in mid-September that it had to be out of MI5’s budget, on the secret vote, and not appear as a War Office expenditure. In that way, as a memorandum in November 1941, stated, ‘no inquisitive persons or committees will be able to investigate it’. Yet, as early as September 1941, a Ministry of Works letter to Abbot drew attention to the fact that the Prime Minister had asked the Production Executive to perform a drastic curtailment of any marginal projects. The official (a Mr. E. Batch) went on: “It is felt here . . . that it is doubtful whether we should proceed with Huntercombe Place”.
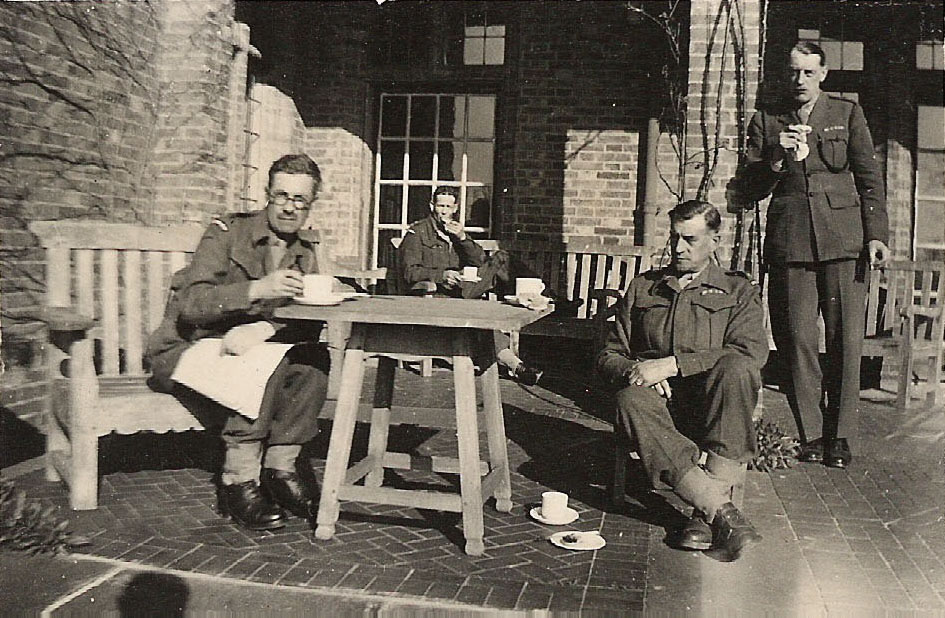

Lord Swinton was able to intervene, however, and the work that had started in late September continued. Batch was summarily taken care of. Construction, and especially the electrical installations, required sentries to guard the property: Latchmere overall was taking on a new existence, and on December 1, David Petrie, the Director-General of MI5, had to rule that the establishment would be separated from B.1.E. on the grounds of its discrete characteristics of Policy, Intelligence, Administration and Army Administration. Furthermore, he declared that “in the interests of Security it is desired that in future Latchmere House, and the Country establishment at Nuffield, shall be referred to in all connections as Camp 020 and Camp 020, R. respectively.’
The Nuffield reference is a fascinating one, in its own right. Nigel West’s suggestion of a larger Nuffield estate, of which Huntercombe Place was a portion, cannot be true. Lord Nuffield (who as William Morris, founded Morris Motors) moved into his house, which was formerly known as Merrow Mount, only in 1933, when he renamed it. One map in the archive shows ‘Merrow Mount’ as a mansion on the right of the entrance road to Huntercombe Place and its much more expansive property. Furthermore, the name of ‘Nuffield’, apart from giving away the location of the new camp, was possibly of some embarrassment, for Lord Nuffield had been a prominent member of the pro-German society, The Link (and is actually listed as such on page 167 of West’s book).
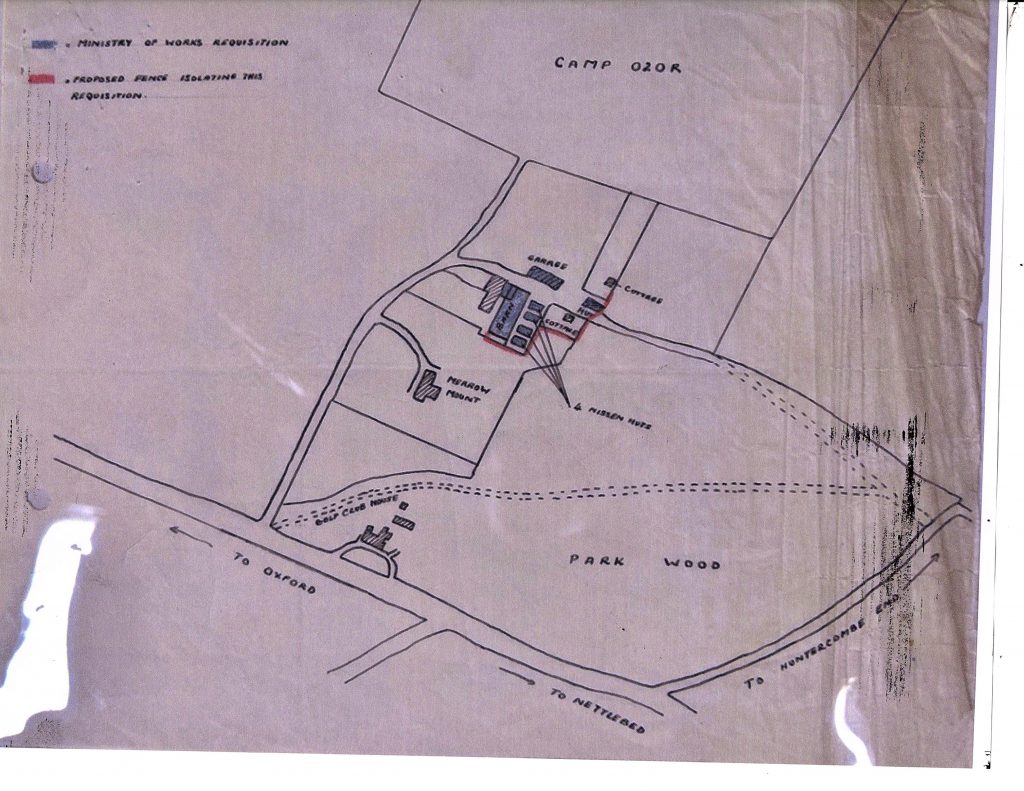
The bills started coming in. An expenditure of £26,500 was marked for the period up to the end of February 1942. The archive is strangely silent for the summer of 1942, but, in August, Lt.-Col Stephens started raising new security concerns, primarily because of the proliferation and extension of USA air-bases in the area. He specifically wanted Huntercombe (and Latchmere) to be declared a ‘Prohibited Area’, where any aliens would be excluded, writing in stark tones: “The fact is that Camp 020 and the reserve establishment 020R are not only contre-espionage [sic] centres, but also prisons where spies who richly deserve the death penalty under the Treachery Act are kept alive for active Intelligence purposes.”
At this point, Stephens made a more exacting demand, suggesting that the camps be handed over to the War Office for administration: “ . . . to discard the appellation ‘Internment Camp’ in each case, and to invite the War Office, from an Army point of view, to administer Camp 020 and 020R definitely as War Office units rather than the responsibility of London District and South Midland Area, by which uninformed and uneven treatment is not unnaturally at times received. Precedents exist in support of this proposal. The first is ‘Camp Z’, which was kept off official lists altogether, and the second is the series of M.I. 19 Intelligence Camps Nos. 10, 20 and 30, which are not only kept off official lists, but are administered by the War Office direct rather than the Military Districts in which they are situated.” This language is rather puzzling – and provocative – as it seems to draw attention to the fact that the legality of Stephens’s establishments may have been questionable.
The irony was that even the MI5 Regional Control Officer, Major M. Ryde, did not know what was going on, and rumours were starting to fly around about the new ‘P.O.W. camp’. The police had taken an interest, but had been refused entry. Even though the place had been requisitioned from the Sheriff of Oxfordshire, the Chief Constable did not know why his officers had been refused admittance. In addition, Stephens had to write about the ‘vast extension’ of the aerodrome at Benson, three miles north, and the erection of a camp for 4,000 US servicemen at Nettlebed, one and a half miles south, which, he believed, would ‘render Intelligence work by special apparatus quite impossible’. Yet he still used the threat of further air bombardment at Ham, and the threat of invasion, as arguments for protecting the ‘reserve’ site.
In the short term, Stephens managed to win this particular battle, it seems, and was able to turn to the problem of staffing. In this he was beset by the problem of whether Camp 020R was going to be complementary to Camp 020, or whether it would still have to absorb all the latter in an emergency. He produced a paper that stressed how important it was to remove the more dangerous ‘old lags’ from Latchmere to Huntercombe. Camp 020 was operationally full in September 1942. Stephens looked forward to Camp 020R opening ‘in the near future’: “I would move there the old lags, split disturbing elements between 020 and 020R, and possibly accommodate some XX prisoners under better conditions.” Who these reformed ‘XX prisoners’ were is rather mysterious, as it hints at several previously unknown spies who could neither be executed nor turned, and Stephens’s desire to house them in better conditions shows a rapid shift in humanitarian impulses from the commandant. In any case, in October, Stephens prepared for the influx. He arranged for Butler to appeal to the War Office that Huntercombe Farm, planned as a domicile for American troops, should be assigned to the Camp ‘for additional accommodation’. Brigadier Harker added his weight to the case in December. New maps of the protected territory were drawn. Another year had passed.
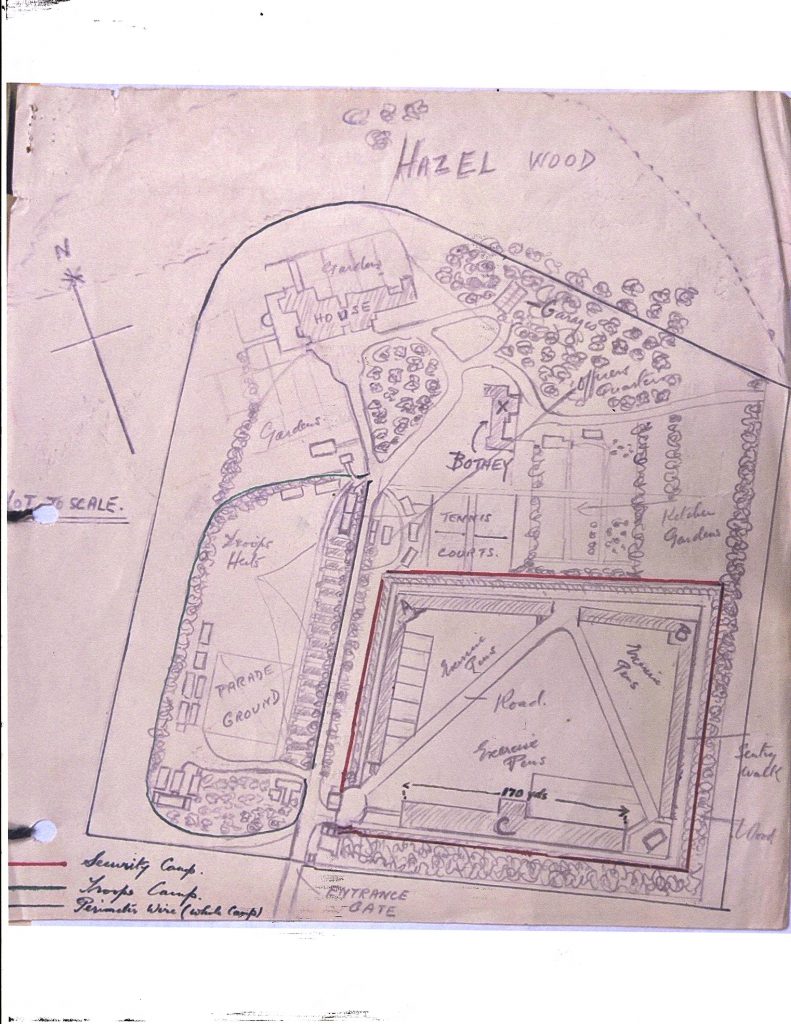
A Change of Mood:
While demands on rural space did not go away, Stephens’ tone continued to change. He softened his objections to low-flying aircraft from R.A.F. Benson. On January 26, 1943, he noted that ‘the threat of a comic Nazi invasion recedes’. Yet now a new bureaucratic challenge emerged – the Home Office, who may have been prodded into action by Stephen’s outburst from August. When MI5 started planning for the transfer of prisoners to Camp 020R in February 1943, it discovered that it had neglected to inform Sir Alexander Maxwell, the Permanent Secretary at the Home Office, even of the idea of the camp. Since Maxwell was very concerned about issues of welfare and fair treatment, Stephens had to prepare a grovelling report, submitted under Petrie’s signature, that stressed how superior the conditions were to those at Latchmere.
Stephens’ words ran as follows: “The conditions at Camp 020 R are more advantageous to the prisoners than at Camp 020 itself. More space is available out of doors, constant association is possible when desirable, while wireless, papers, games, cigarettes and other privileges are provided free of charge. Rations are somewhat better than received elsewhere as we are able to supplement the prescribed scale by produce form the ground.” This was far from the notions of ‘oubliettes’ and ‘prisoners being kept alive’: a concern now focussed on prisoners’ welfare. It sounded as if the ‘country establishment at Nuffield’ was taking on the characteristics of a country club, or health farm.
Moreover, the emphasis is no longer on ‘reserve’, even though the two camps are to be considered as one entity. Stephens told Maxwell that the camp was to be used ‘primarily as a place to which we can send prisoners whose intelligence investigations have been completed at Camp 020 and who, because of the espionage nature of their case, cannot, for security reasons, be transferred to any ordinary internment camp, or other place of detention.’ He was no doubt thinking of agents who had not been successfully turned, and thus knew too much about the Double-Cross System, such as SUMMER. Yet SUMMER had had to be re-confined well before Camp 020R was ready to accept prisoners.
The Home Office Wakes Up:
Standing orders were issued for the reception of internees on November 10, 1942, and prisoners started arriving in January 1943, it seems. (On the other hand, documents in KV 4/103, such as those referring to unauthorised lending of library-books between prisoners [!], indicate that detainees were already being held there.) Soon some ‘incident’ must have occurred, probably of maltreatment, since Harker had to intervene, but possibly an attempt at suicide by one of the detainees. The full documents have been removed, but the Register holds a memorandum from the Deputy Director-General, who had to seek a meeting with Maxwell to ‘explain what had happened’. “I further made it quite clear to Sir Alexander Maxwell that Mr. Milmo was in no way responsible for what had occurred, and I feel sure that his position will not be imperilled in any way by reason of any premature action”. But what had ‘Buster’ Milmo done? Liddell went on to write that Maxwell confirmed Milmo’s view that ‘the persons transferred to 020(R) are illegally detained’. A flurry of activity resulted in a report for Maxwell’s benefit.
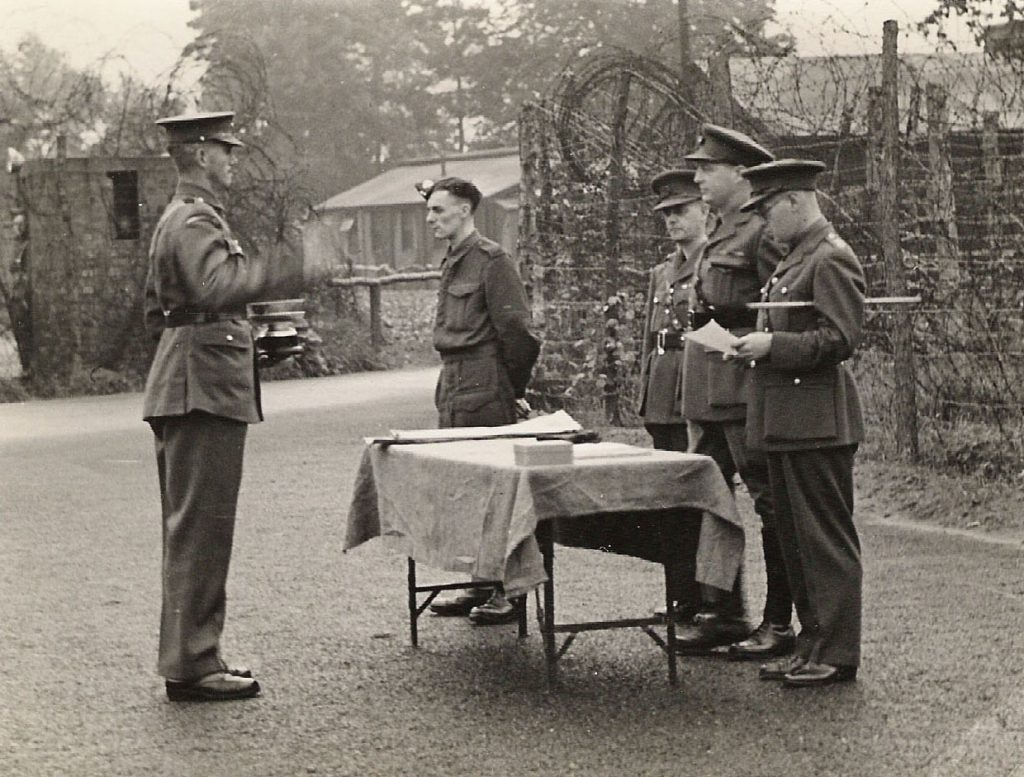
The legal basis for the camps thus had to be investigated, and was eventually determined. In an instrument dated March 20, 1943, Camp 020 was ‘formally authorised as a place of detention for persons held under Articles 5A and 12(5A) of the Aliens’ Order’, and the Home Secretary then signed an equivalent order for Camp 020R (thus, incidentally, undermining the argument that the two camps should be seen as one unit.) But the Home Office also found a loophole: there was no formal authorisation for those detained under D.R.18B and 18BA, namely arrested spies, and the Home Secretary had to sign an order with retroactive effect, to cover this situation. Sampson informs us that Home Secretary John Anderson had given Swinton a ‘verbal’ [he should have written ‘oral’] approval during a telephone call in 1940, but had clearly not discussed the matter with his civil servants.
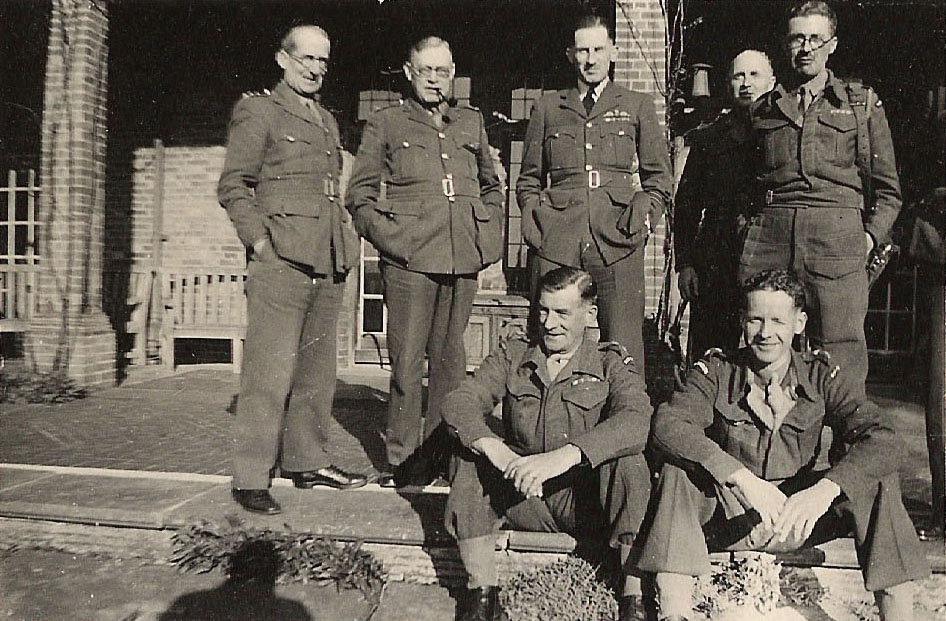

[Lt.-Col. Sampson second from left. Is that a senior RAF officer in the centre, maybe visiting from R.A.F. Benson? Looks a bit like the future Marshal of the R.A.F. Arthur Tedder, but then perhaps all Air-Marshals looked like Tedder.]
Apparently the transferred prisoners were not happy with their lot, as they started sending in petitions to the Home Secretary in the summer of 1943. Whether the more comfortable conditions at Camp 020, and the availability of books, had contributed to their sense of entitlement, or whether they had been put up to it by some champion for them, is not clear, and the record is sparse. But in August 1943, Milmo (B1B) had to respond to a complaint from the Home Office, which was obviously perturbed by the volume of petitions coming to it. “As has been pointed out”, he wrote, “the amenities at Camp 020R leave nothing to be desired, and are of an exceptionally high standard, being more reminiscent of a modern hotel than an internment camp.” He went on to explain the comforts, freedom of movement and association, no forced work, gardening optional, free tobacco, etc. etc. , and concluded: “We are quite satisfied that these manifestoes are the result of something in the nature of a conspiracy, and this is borne out by the fact that there were no signs of unrest or disturbance of any kind at the camp.”
When Maxwell held a meeting, on July 29, to discuss the administration of Camp 020R, Petrie himself attended, confirmed the fact that both Dr. Dearden and a local practitioner were available for medical attention. (Here also is the first indication that Camp 020R had its own commandant, a Major Gibbs.) The last item informs us that ‘such matters as attempts at, or actual, suicide would be so reported’, thus confirming the ‘incident’. Petrie followed up, somewhat sluggishly, on November 29, by inviting Maxwell to visit Camp 020R, so that he might investigate working conditions for himself. He reminded Maxwell that a ‘considerable number’ of ‘detainees’ had been transferred to Camp 020R, and that he expected several more in the coming months. Some jocularity was now called for: “I think you will also be interested in the ‘amenities’ which are provided at Stephens’ ‘country’ residence!”.
Petrie had visited the camp just before he sent this letter, and a memorandum from Butler to Stephens, dated December 1, reminds the latter that he and Petrie were both keen that ‘more books and games’ should be made available for the prisoners, and that money was on hand to address this need. The ensuing flurry of memoranda shows the earnestness with which this project was pursued, and also informs us that ’well over 100’ internees were now present there, of which half knew little English. Maxwell, meanwhile, was highly occupied, and replied on December 16 that he would not be able to accept the invitation until January.
So yet another year passed. Maxwell visited Camp 020R on January 5, and wrote promptly to Petrie the next day. In a somewhat starchy and headmasterly way, he requests Petrie to make sure that the Home Office receives a copy of any report made after a prisoner complaint. He is evidently concerned that he is ultimately responsible for the treatment of the prisoners, but has not been kept properly informed. Stephens’ instructions to Butler, a few days later, indicate that Milmo has been following the book over such cases, and the problem was probably due to civil servants in the Home Office suspecting that facts were being withheld. Stephens takes the time to remind Butler that Maxwell was otherwise very impressed.
The final note in the first file on Camp 020R shows that Maxwell has bought into the idea that Camp 020R was ’not an ordinary internment camp’. In a memorandum to Petrie, Butler reports on a meeting he had with Maxwell, where the latter ‘entirely agreed that it was extremely important that as few people as possible should know the details of the cases at Camp 020 and Camp 020R, or indeed of their existence. In the preparations for D-Day it was essential that no leakage of information about the so-called ‘double agents’ should occur.
Stephens’ assessment of Camp 020R was somewhat mournful: “There the prisoners learnt much about the British Constitution; they whiled away their time by writing petitions to the King, to the Home Secretrary and to the Judges. Sometimes they gave good advice to Mr Churchill and Mr Anthony Eden. Occasionally they tried to escape. In the end it became a soulless camp, and much sympathy is due to the officers and men who carried out their dreary task so conscientiously and well for so long a time.” Peter Mackean has pointed out to me how these obligations endured for several years after the war.
Camp 020R in Operation:
The second file, KV 4/103, covers Camp 020R after it opened for business at the beginning of 1943. It is not very revealing. It is replete with standing orders, such as the posting of sentries, fire precautions and orders, inspections, and instructions for distributing newspapers and cigarettes, bathing protocols, cell cleanliness, exercise, and the procedures for escorts and vehicle searches. The Home Office is clearly very interested in the welfare of the internees, who are now granted rights that one might deem over-indulgent for such a group of desperadoes. “Complaints, couched in respectful language, will be in writing and will be handed by prisoners to the Orderly Officer of the day at breakfast rounds only”, runs one edict.
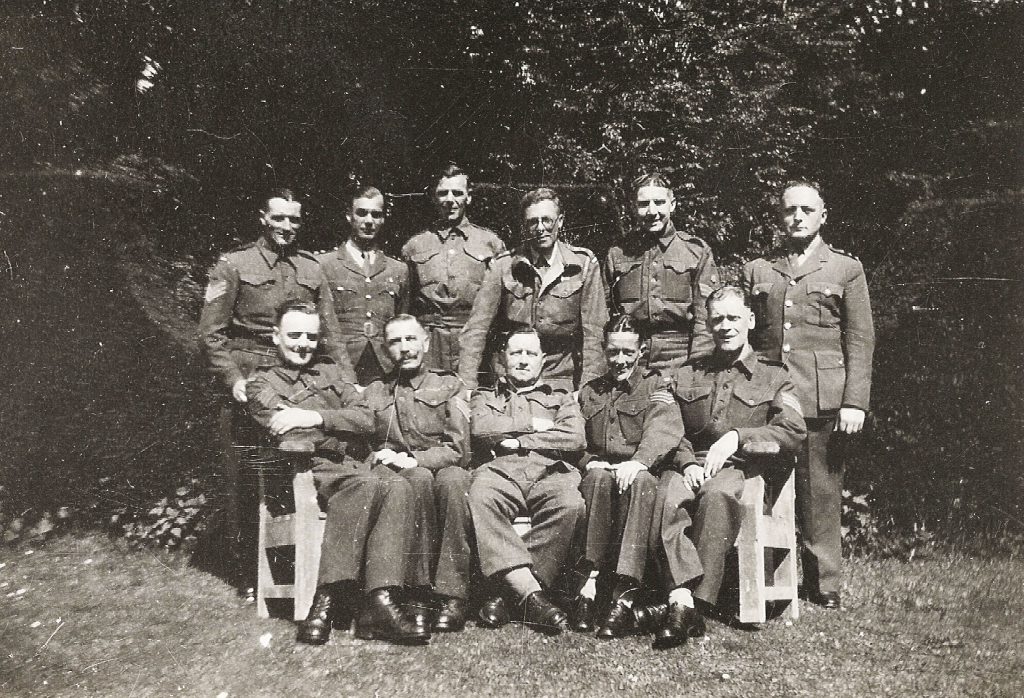

By early 1944, the permanent secretary at the Home Office, Sir Alexander Maxwell, has visited the camp, and is overall satisfied, but he is concerned about extra medical supplies, and wants the chief prison Medical Officer, Dr. Methven, and Sir John Moylan (who appears to be responsible for handling petitions) to visit the camp at Huntercombe. Stephens is concerned about security and disruption. Maxwell seeks extra milk for prisoners having medical problems, a concern that Stephens has to address himself, and informs Milmo back in Head Office. Petrie is involved in the question of extra nourishment that ‘may be required for medical grounds’. One wonders: did these gentlemen not know that there was a war on?
Despite all this attention to their wellbeing, prisoners still planned escapes from their Colditz-in- the-Cotswolds, as a letter of February 21, 1944 confirms. The detainees involved were Stephens, K. C. Hansen, Pelletier, Hans Hansen, Oien, Olsen, Robr, Ronning, Steiner [sic], and Lecube – not all of whom, somewhat mysteriously, appear in the list maintained, and later distributed, by the camp authorities. But Stephens was on top of it, and wrote to Richard Butler on February 23: “I am not in the least troubled by the situation at Camp 020R. the men involved are determined to escape and the authorities concerned are equally determined that they will not succeed.”
Another year passed, apparently peacefully, and at the end of May 1945, Stephens planned to liquidate both Camp 020 and Camp 020R at once. He was alert to the constitutional challenges, and firmly believed that, no matter how ill-prepared their native countries might be, the prisoners should be repatriated at once. He wants some detainees at 020R to be sent to Camp 020, and sets a target of June 15 for Camp 020R to be closed. All prisoners were in fact moved to Ham by July 3, and the property was handed over to the Ministry of Works later that month, and its closure formally declared on September 5. Those German prisoners captured towards the end of the war who had been brought initially to Ham (such as Karl Heinz Kraemer, who played a very significant role in Stockholm) were transferred to Diest in Belgium, and then Bad Nenndorf, camps which were managed by the Ministry of War, not MI5. Camp 020 was disbanded in December, although Petrie did report to Maxwell that ‘a small residue’ of detainees were still in Beltane Schools [sic: a school originally for German Kindertransport children, in Wimbledon], awaiting repatriation.
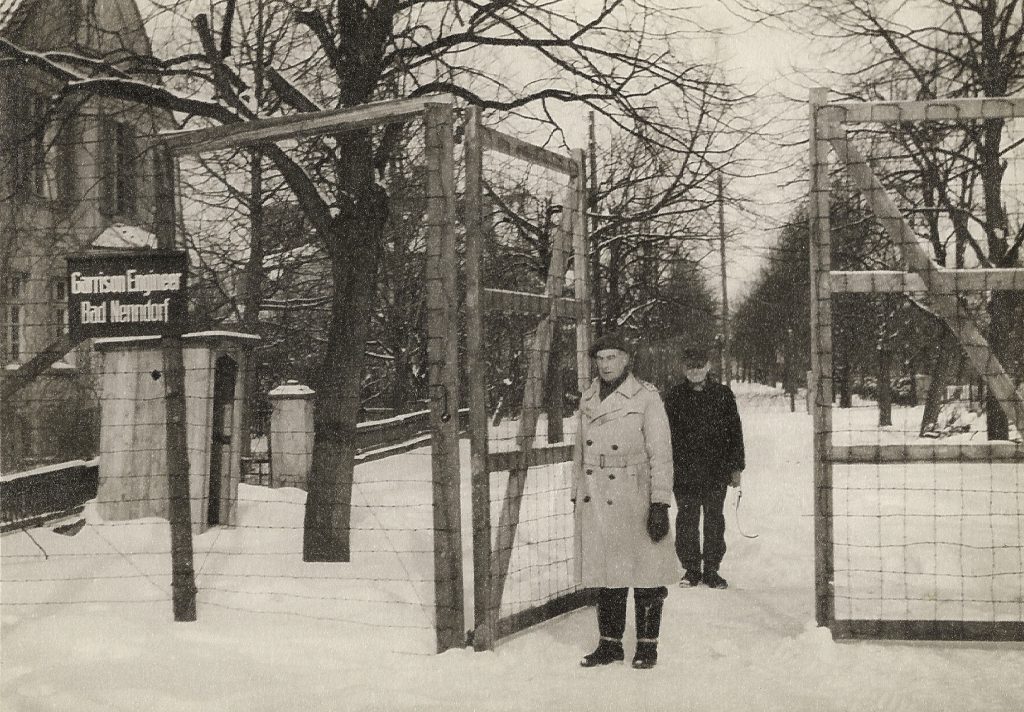


After the war, Camp 020R became a Borstal prison. In 1983, it became a cellular prison for young juveniles. It has since (according to Wikipedia) taken a role for holding foreign national offenders awaiting deportation – an echo of its wartime role. Huntercombe Hall, which was used for administration, and as a recreational and residential facility, is now Huntercombe Hall Care Home, owned by Oxfordshire County Council, which offers ‘residential, nursing, and dementia care for up to 42 elderly residents’.
Thus the installation has come full circle, and acts as a stark reminder of the legal and constitutional challenges facing a security service and police force that today have to protect the democracy from hostile elements planning mayhem, but who may have not committed any act that can confidently be prosecuted.
The Prisoners:
Stephens’s commentary in his history, and a Kew file (KV 2/2593), combine to give us a good description of those who were moved to Camp 020R. I list them here, with a brief thumbnail sketch of those for whom information exists.
Stoerd Pons Only member of his LENA spy squad to escape execution
Gosta Caroli SUMMER: reneged, tried to escape by overpowering his guard
Kurt Goose Double-agent who tried to smuggle message to German Embassy
Albert Jaeger
Otto Joost LENA spy who was spared
Gunnar Evardsen LENA spy who was spared
Cornelius Evertsen Dutch captain who tried to land agents in Fishguard
Arie Van Dam Member of Belgian sea-mission in London; denounced
Theophil Jezequel Cuban from Spain recruited by Abwehr; brought in by Evertsen
Juan Martinez ditto
Silvio Robles ditto
Pedro Hechevarria ditto
Kurt Hansen
Gerard Libot
Wilhelm Heinrich
Hugo Jonasson Swedish skipper recruited by Abwehr in Brest
Francis de Lee
Jan de Jonge Dutchman arrested in Gibraltar making inquiries about convoys
Jose del Campo Cuban arrested in British port, confessed
Karl Hansson
Johan Strandmoen Norwegian arrested in Wick on ‘fishing’ expedition
Bjarne Hansen ditto
Hans Hansen ditto
Henry Torgesen ditto
Edward Ejsymont Pole form Gdansk who made misleading statements
Helmik Knudsen
Edward Balsam Polish Jew who shadowed Ejsymont; made false claims?
Abraham Sukiennik ditto
Eigil Robr Norwegian traitor spirited into UK by military attaché in Stockholm
Leopold Hirsch Crook who tried to bribe Germans captured in Trinidad
Oscar Gilinsky ditto
Gustav Ronning
Martin Olsen
Thorleif Solem Norwegian in pay of Germans arrested in Shetland Islands
Sigurd Alsaeth ditto
Cornelius Van der Woude
Florent Steiner Belgian seaman denounced by Verlinden
Piet Schipper Dutch seaman engaged by Abwehr
Jean Pelletier
Gottfried Koch
Erich Blau
Hans Sorensen
Carl Meewe
Hilaire Westerlinck Belgian doctor denounced by Verlinden
Tadeus Szumlicz Polish refugee recruited by Germans in Paris
Jens Palsson
Leon Jude Belgian airline pilot recruited by Germans
Robert Petin Frenchman in air force who retracted his confession
Alfred Lagall
Jose Manso Barras
Sandor Mocsan Hungarian employed by German in Brazil: radio interception
Janos Salomon ditto
Sobhy Hanna Egyptian groomed by Abwehr, arrested in Dar-es-Salaam
Pieter Grootveld
Pierre Morel Demobilised French pilot, employed by Germans: evasive story
Serrano Morales
Juan Lecube Mulish Spaniard, arrested in Trinidad: radio interception
Jose Moreno-Ruiz
Vincente Fernandez-Pasos
Gabriel Pry Belgian mathematician: offered services to Abwehr, arrested in Lisbon
Ernesto Simoes Portuguese spy in UK who contacted Germans by secret ink
Dos Santos Mesquita Portuguese journalist captured in Lourenço Marques
De Ferraz Freitas Portuguese radio operator on fishing-fleet: radio interception
Garcia Serrallach Petty Argentinian crook captured in Trinidad
Andres Blay Pigrau ditto
Homer Serafimides Greek seaman, swindler: handed over to British in Durban
Torre de la Castro
Frank Stainer Belgian crook Abwehr planned to infiltrate, captured in Lisbon
This is a mixed bag of scoundrels. Clearly some of them deserved the death penalty, but MI5 was reluctant to invoke the Treachery Act, as it would mean public trials, and secrets coming out that the service would prefer remain hidden, followed by an obligatory death sentence if the accused had been found guilty. There might be further information to be gained by interrogation, and, if too long a time passed, questions would be asked why there had been a delay. A few were failed ‘double-agents’ who knew too much. Some of the accused had been denounced, and motives might have been suspect; the identity of others had been gained by interception of Abwehr radio signals (ISOS), and clearly had to be kept quiet. Lastly, many of those detected had been arrested on foreign soil. The jurisdiction that the UK security service had over such probable criminals was uncertain, and many such persons had therefore to be detained until the end of the war, when they were repatriated to their home countries so that they could receive native justice. At least one (Stainer) was executed under such circumstances.
* * * * * * * * *
Now that the Presidential election is over and decided (pending last-minute judicial challenges), we have to look forward to the period of transition. We thus need to build a word-ladder from TRUMP to BIDEN.
A word-ladder is a set of words that incorporates a change of one letter at a time to transform the subject word into the object word, where no proper names are used. Thus MOAT can become HILL by a sequence such as MOAT-MOOT-HOOT-HOLT-HILT-HILL.
I have discovered a ladder of 14 steps to take TRUMP to BIDEN (i.e. thirteen intermediate ‘rungs’). And I have created another 14-step ladder to transform TRUMP to PENCE, as the Republican chief in waiting. However, if we want to project the transition to my favourite for the 2024 Republican presidential nominee, Nikki Haley, I have plotted another 14-step campaign for TRUMP-HALEY. On the other hand, sketching the 2024 handover from BIDEN to HALEY is a 6-step breeze. I am offering an extended free tour of my library to anyone who can offer a combined array shorter than these, a 48-step total. And I can promise that my library is far more interesting than the Donald J. Trump Presidential Library ever will be, as the latter will probably contain just bound volumes of Playboy, and signed copies of The Art of the Deal. Please send your answers to antonypercy@aol.com. (Travel and accommodation arrangements are the responsibility of the winners.)
New Commonplace entries can be found here.

Denis Lenihan has pointed me towards the phenomenon of the Wartime Rules at Richmond Golf Club, next to Latchmere House. See: https://www.therichmondgolfclub.com/wartime-rules/
Hello,
Thank you for this very intresrting work. a question, which is not very elaborate: what were the living conditions in concrete terms at camp 020 and 020R? For example, what could be a typical day for a detained person? On the other hand, was there a difference in treatment between the XX agents and the others? Finally, to what extent were the inmates able to communicate with each other? Were they separated by profile types?
Thank you for your answers
D.
Thank you so much for posting, Dominique.
I regret that I cannot help you much, as I really did not study those aspects, and it would probably require someone who has trawled through various memoirs.
The Public Record Office (now the National Archives) published a book, ‘Camp 020’, with an Introduction by Oliver Hoare, that contains much of the official records, including potted histories of many of those detained, which you may find useful. Helen Fry (hpfry@btinternet.com) wrote a book ‘The London Cage’ about the Interrogation Centres: her bibliography may be useful to you, or you might like to contact her directly.
Tony.
I think we should keep some aspects in perspective considering the time at when these prisoners were kept in captivity, those being very different to today
I think once initial interviews were conducted it could be determined who these people were, good or bad, those being bad would be interrogated further and kept in Camp 020, if they were no longer required, or considered low risk, but still required to be detained they were moved to Camp 020R at Huntercomb, and also to avoid the London bombings
Its my understanding, in spite of the troubled times that measures were taken to keep prisoners occupied, with reading material in their own languages, news papers were probably not aloud in order to keep the prisoners from being informed of what was going on outside, feeding them information
But at Huntercomb there was a prisoners garden where they were able to grow much needed vegetables used in the kitchens, becoming a little more sustainable would lead to a healthier prisoner
But on the whole i suspect keeping prisoners under observation, segregated from each other, would likely take it toll on some individuals, prison was not so much the bad thing
The initial ideas and suggestions that all prisoners were tortured, i feel is very much hear say, yes times were very difficult, Tin eye Stephens himself was investigated and found not guilty and later awarded his OBE for his services – sure a few folk sadly passed away in unfortunate circumstances, mush to do again with the times, millions of people displaced in war time, food was poor, conditions were poor due to insufferable winters, coal shortages – i’m sure feeding such prisoners might be a lower priority in some cases, but making sure these kind of Nazi’s were made accountable for their actions was more important and keeping them alive would be paramount
As with all organizations, their will be examples of cruelty as their indeed seems to be with the London Cage – i believe from my own research that Stephens conducted a good cop bad cop operation and well deserved his OBE – my grandfather Charles MacKean spent a further four years in Germany after the war ended, his war continued in a war torn country, those times could not be easy on anyone and i think we should not forget this
I found this a fascinating read and very well researched, so thank you on both counts.
I was intrigued by the reference to interment camps in or around Liverpool. This is my home city but I know nothing of this. Do you have any further information or suggestions of where to look for this please?
On a personal note, I prefer footnotes to endnotes myself as I find that having read something, I am less likely to refer to an endnote since this means breaking my concentration on the main text and loosing the thread, but that is a personal thing.
Thanks, Nigel.
I regret that I cannot add anything to what I wrote here. I similarly searched for a comprehensive list. You might want to contact Helen Fry, who wrote ‘The London Cage’ (hpfry@btinternet.com)
I agree about Endnotes and Footnotes. Unfortunately, too many writers overdo the Footnotes, when text could either be absorbed in the main line, or relegated to an Appendix. Endnotes are necessary for the serious researcher to follow up.
Tony.
Thanks Tony – I will follow up your suggestion.
I was intrigued also by the idea of using Liverpool University as a “dumping ground” for spies or the like but have yet to read that article.
Hello,
Thank you very much for an excellent and detailed piece on these two internment camps.
My Grandad was involved in interrogating German spies in a facility somewhere near London at this time. He had served in the RFC/RAF in WWI and was presumably recruited as he was a fluent German speaker. Because he had signed the Official Secrets Act he divulged very little during his lifetime about where he worked and what exactly he did. We think he held the rank of captain and we know he travelled to mainland Europe after the end of of the war in 1945 in his officer’s uniform. My Dad met up with him in the southern Netherlands at the time. I suspect he may have well travelled to Diest or Bad Nennberg.
From the little he told one of my cousins, he said he was involved in interrogating a group of spies and spoke about some of the techniques they used to get them to talk. I think it is possible that he was involved in interrogating the group with Jose Walberg.
According to the book on Camp 020 (p368), 25 Intelligence Officers worked at Camp 020. Are you aware of any records with their names and details of their work there?
I have written to MI5 and they have confirmed that he did not serve with them as an Intelligence Officer. I have also written to Helen Fry, who thinks he would likely have been recruited into the Army to do this work. There is nothing in his military record about this.
I look forward to hearing from you.
Reinout Mildner
Thank you, Reinout, for your comments and interest!
This was a while back, and I cannot recall whether I used any other archival material apart from the files listed. The only way I know of picking up the kind of information you seek is to trawl through the files, and personal records of the inmates (if they have been released), searching for clues. I have used this technique to start building an Index of otherwise unidentified PF numbers for various characters – hundreds of them – that MI5 kept tabs on.
Best of luck!
Tony.